Problem Overview
We are given an array heights of size n.
The value at each index represents the height of a vertical bar.
We need to find two bars such that together they can hold the maximum amount of water.
Note: We are not allowed to slant the container.
LeetCode - Container With Most Water
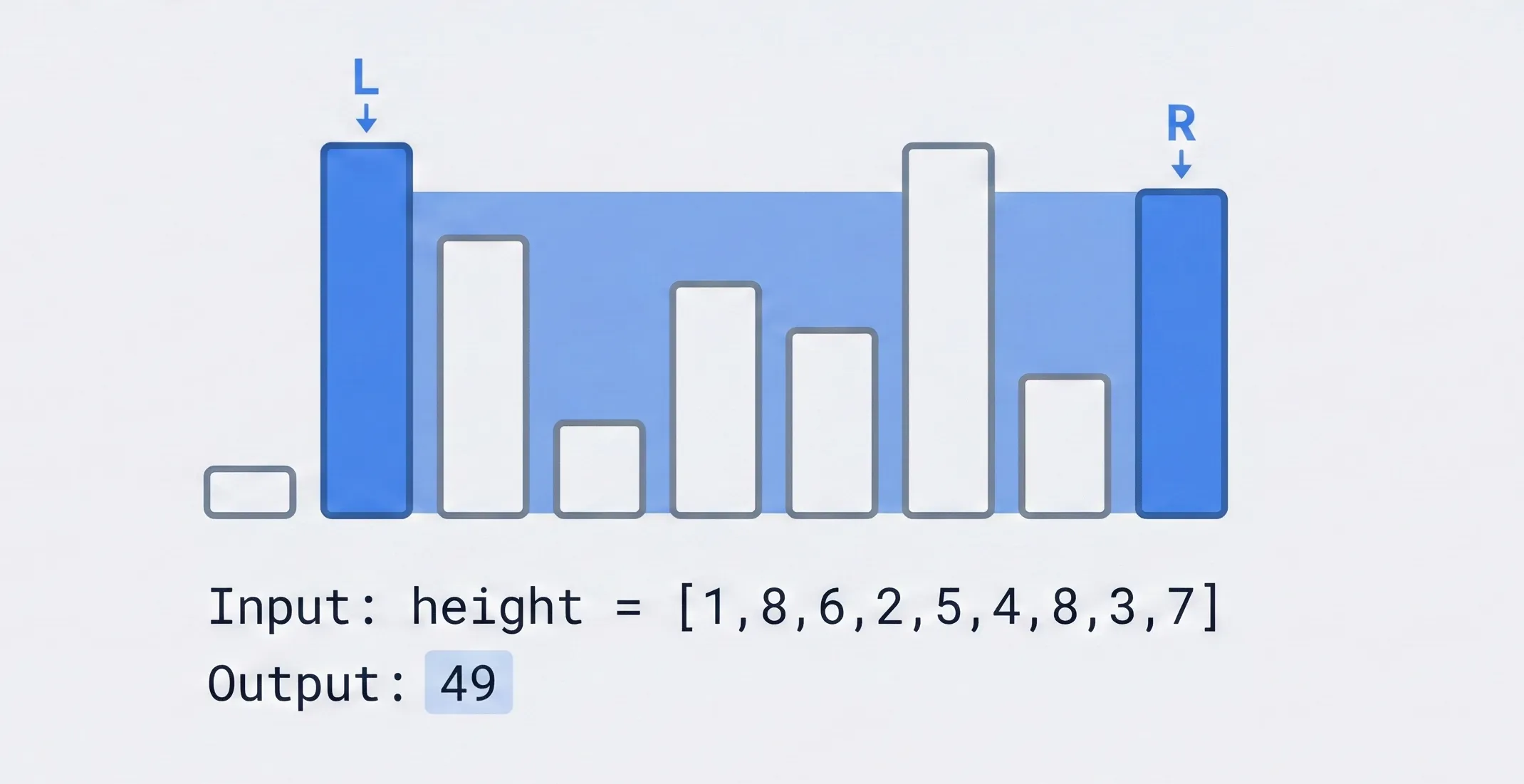
Example
Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
Greedy Logic Attempt
The idea was inspired by Kadane’s Algorithm
- Track maximum height so far.
- Compute area at every step.
- Maintain
maxSoFar.
Code Attempt
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxIndex = 0;
int maxSoFar = 0;
int n = height.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(maxHeight < height[i]){
maxHeight = height[i];
maxIndex = i;
}
maxSoFar = min(maxHeight, height[i]) * (i-maxIndex);
}
return maxSoFar;
}
};
Why This Fails
The container area depends on height and width:
- Height →
min(height[i], height[j]) - Width →
j - i
Problems with the greedy approach:
- We fixed one side of the height.
- A slightly smaller height with much larger width can produce a bigger area.
- Not all valid pairs are checked.
Optimal Solution – Two Pointer Approach
Idea:
- Start one pointer at the beginning (
l = 0) - Start the other at the end (
r = n - 1) - Calculate area at each step
- Move the pointer that has the smaller height
Why Move the Smaller Height?
Area formula:
Area = min(height[l], height[r]) * (r - l)The smaller height is the limiting factor.
Moving the taller height won’t help because:
- Width decreases
- Height limit doesn’t improve
Only moving the smaller height gives a chance of finding a taller boundary
Code – Two Pointer Approach
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {
int maxSoFar = 0;
int n = height.size();
int l = 0, r = n - 1;
while (l < r) {
int area = min(height[l], height[r]) * (r - l);
maxSoFar = max(maxSoFar, area);
if (height[l] < height[r]) {
l++;
} else {
r--;
}
}
return maxSoFar;
}
};
Time and Space Complexity
- Time: O(n)
- Space: O(1)
Final Takeaways
- Maximum area is not only about maximum height.
- Width plays an equally important role.
- When a problem involves two boundaries and width between them, think about two pointers.
- Failed attempts are not wasted — they help you understand constraints better.