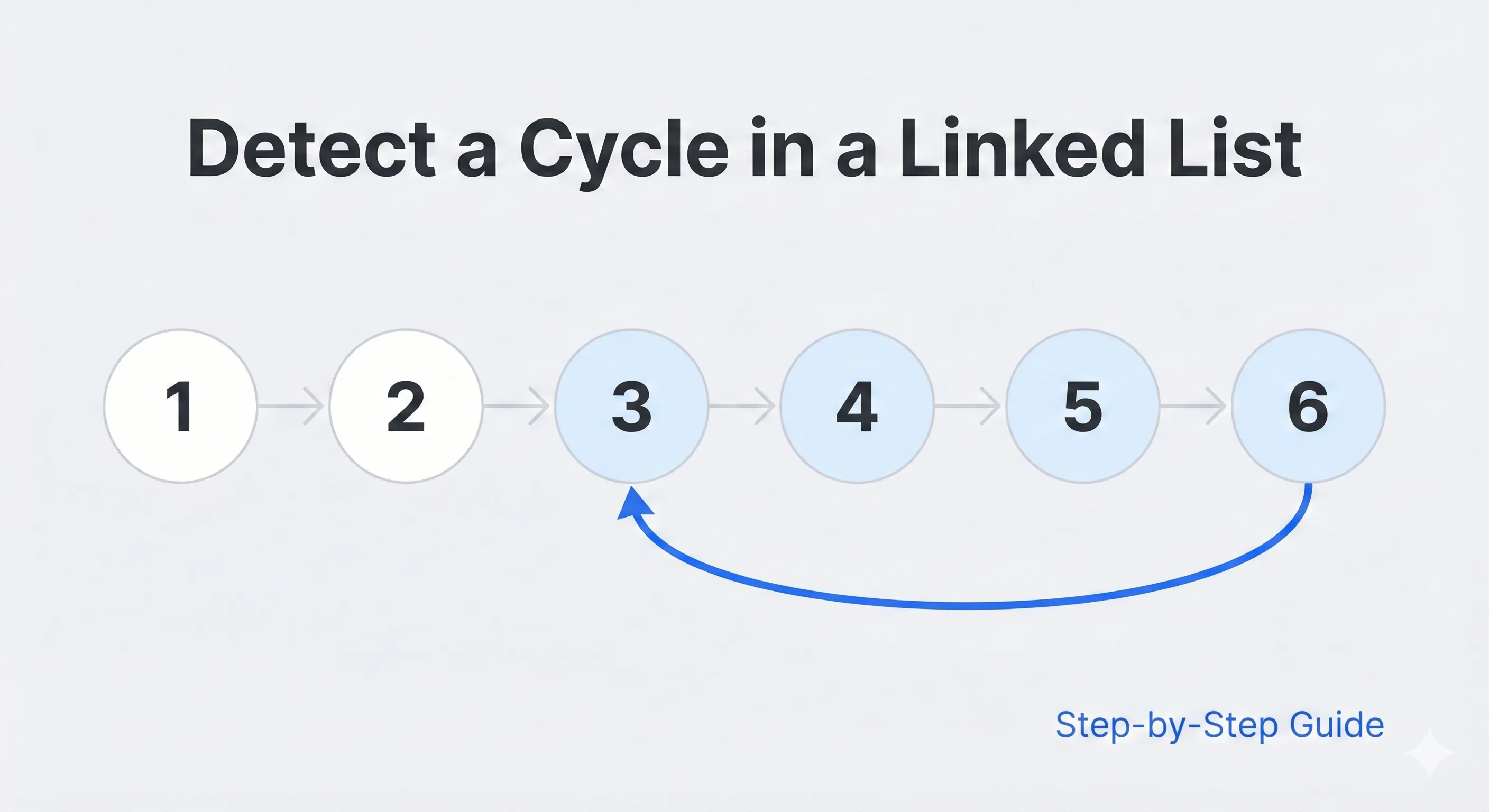
Problem Overview
We are given the head of a singly linked list. We need to detect if a cycle is present in the list or not.
Follow-up: Solve this in constant space.
Example
3 → 2 → 0 → 4
↑ ↓
└─────┘
As the last node 4 is linked back to 0, a cycle is present.
Brute Force
Intuition
The idea is to store each node in a map. While iterating, if we encounter the same node again, there is a loop.
Code
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode* head) {
if (!head)
return false;
unordered_map<ListNode*, int> mp;
ListNode* curr = head;
while (curr) {
if (mp.count(curr)) {
return true;
}
mp[curr]++;
curr = curr->next;
}
return false;
}
};
Why This Works
- Keep track of each node as we pass through it.
- If we see the same node again, then there is a loop.
Why It Fails
- The problem asks to solve this in constant space.
- This approach uses extra memory.
Time & Space Complexity
- Time: O(n)
- Space: O(n)
Optimal Approach
Floyd’s Cycle Detection (Tortoise & Hare)
We use two pointers:
slow→ moves one step at a timefast→ moves two steps at a time
If there is a cycle, they will eventually meet at some node inside the cycle.
If there is no cycle, fast will reach NULL.
Dry Run
3 → 2 → 0 → 4
↑ ↓
└─────┘
Cycle starts at 2.
Initial State
slow = 3
fast = 3
Visual:
(3) → (2) → (0) → (4)
↑ ↓
└───────────┘
S,F at 3
Iteration 1
Move:
- slow → 2
- fast → 0
Visual:
(3) → (2) → (0) → (4)
↑ ↓
└───────────┘
S F
Positions:
slow = 2
fast = 0
Iteration 2
Move:
- slow → 0
- fast → 2
Visual:
(3) → (2) → (0) → (4)
↑ ↓
└───────────┘
F S
Positions:
slow = 0
fast = 2
Iteration 3
Move:
- slow → 4
- fast → 4
Visual:
(3) → (2) → (0) → (4)
↑ ↓
└───────────┘
S,F
They meet at node 4.
Code (Optimal)
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode* head) {
if (!head) return false;
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast)
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
Time and Space Complexity
- Time: O(n)
- Space: O(1)
Final Takeaways
- Tortoise & Hare method is the most efficient method to detect cycle in the linked-list
- Instead of map we can also use set