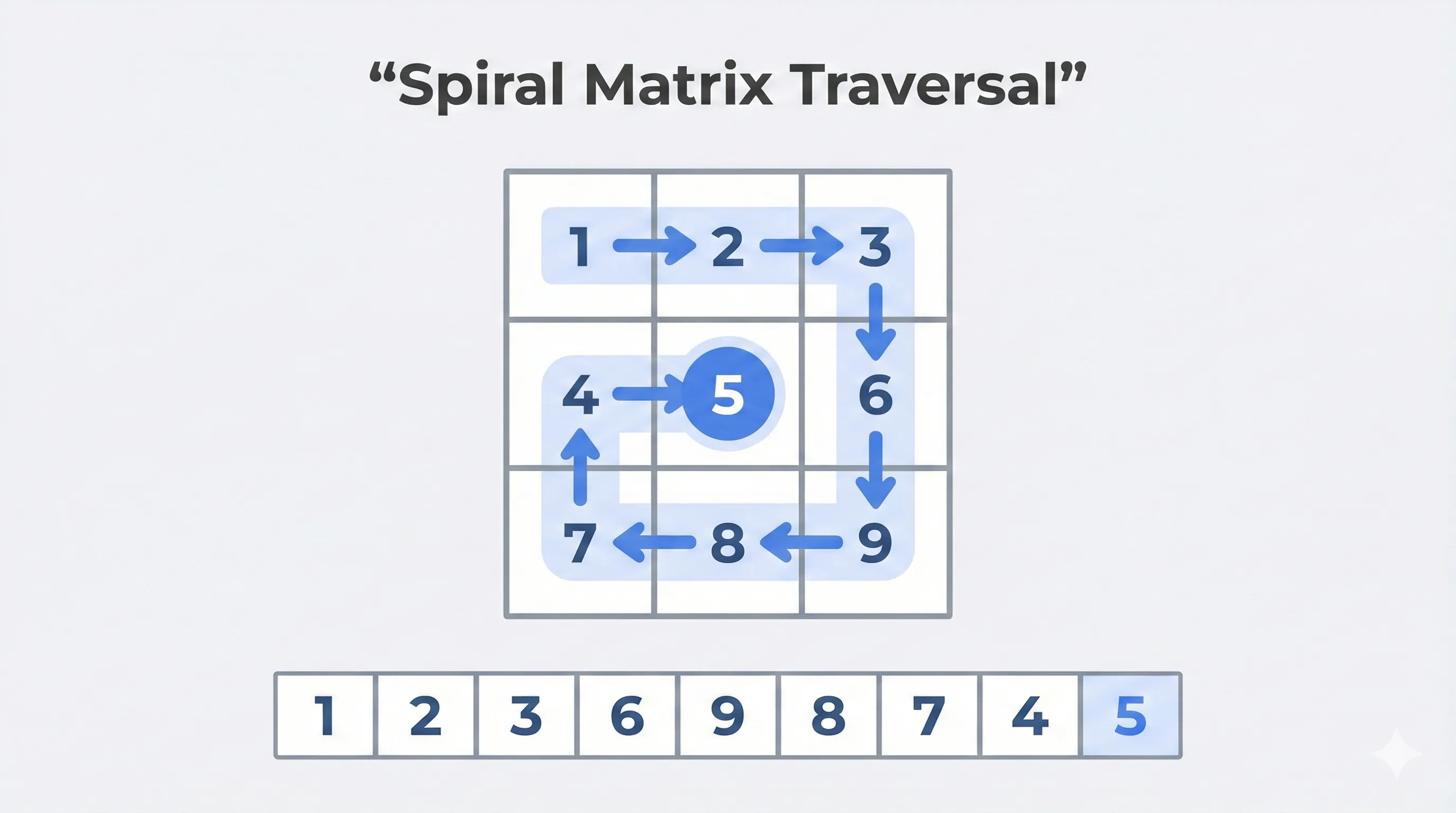
Problem Overview
- We are given a matrix of size
m * n. - We need to return all elements of the matrix in spiral order.
- Note: The matrix is not necessarily square.
Example
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9]]
Output: [1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
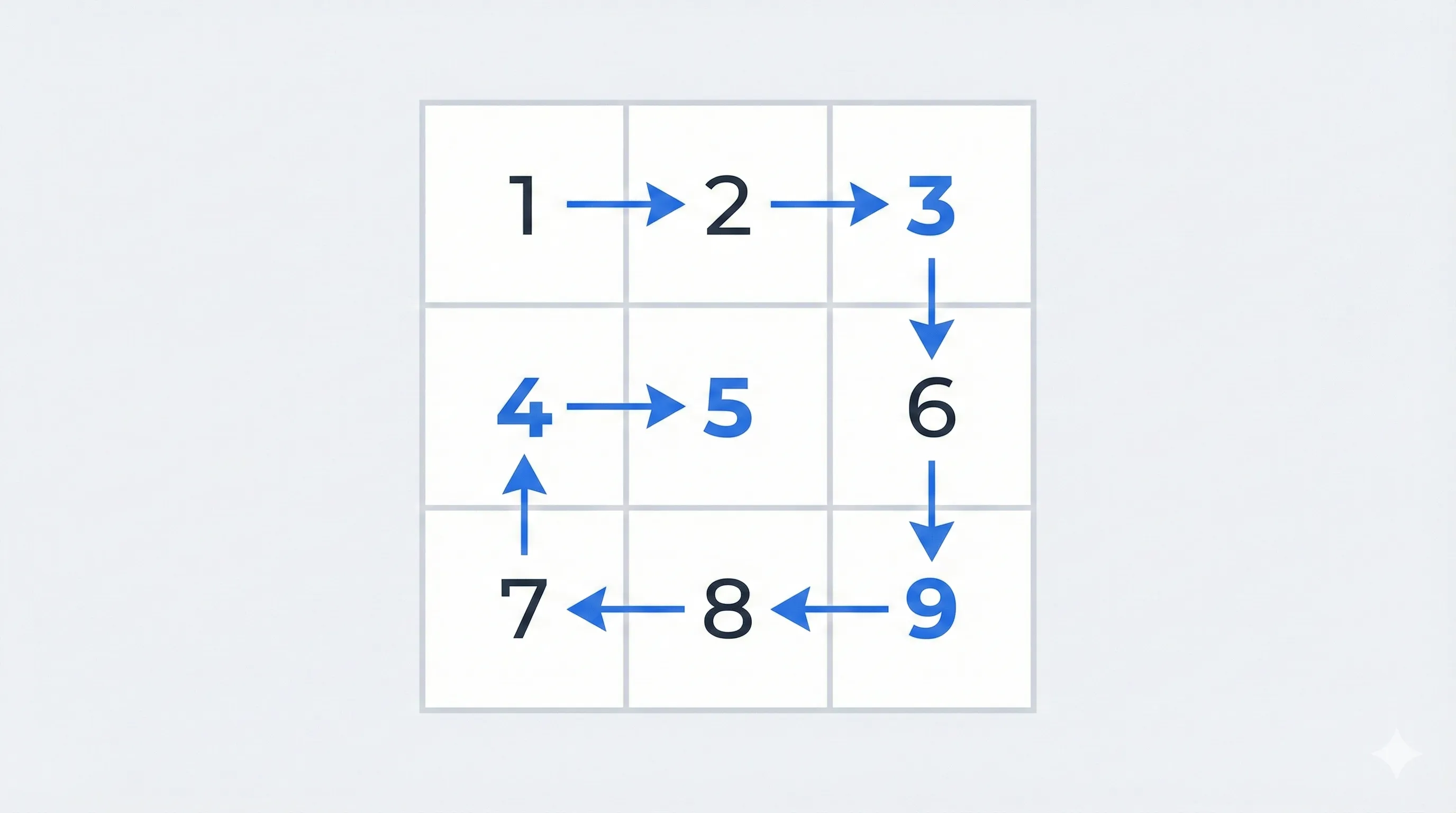
Intuition
We need to travese the matrix in this order
Indices traversal:
(0,0) → (0,1) → (0,2) right
(0,2) ↓ (1,2) ↓ (2,2) down
(2,2) ← (2,1) ← (2,0) left
(2,0) ↑ (1,0) up
(1,0) → (1,1) right
So the movement pattern becomes:
(top, left) → (top, right) | move right
(top, right) → (bottom, right) | move down
(bottom, right)→ (bottom, left) | move left
(bottom, left) → (top, left) | move up
Observation:
- If we repeat this pattern and shrink the boundaries after each cycle, we can cover the entire matrix.
Optimal Solution
Approach
Maintain four boundaries:
topbottomleftright
At every iteration:
- Move left → right (top row)
- Move top → bottom (right column)
- Move right → left (bottom row)
- Move bottom → top (left column)
After each direction, shrink the corresponding boundary.
Important Edge Cases
Always check:
top <= bottomleft <= right
Reason: After shrinking, an extra invalid iteration can happen.
Without these checks, elements may get duplicated.
Code Implementation
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
int m = matrix.size();
int n = matrix[0].size();
vector<int> result;
int top = 0, left = 0;
int right = n - 1, bottom = m - 1;
while (left <= right && top <= bottom) {
// Move left to right
for (int col = left; col <= right; col++) {
result.push_back(matrix[top][col]);
}
top++;
// Move top to bottom
for (int row = top; row <= bottom; row++) {
result.push_back(matrix[row][right]);
}
right--;
// Edge Case Check
if (top <= bottom) {
// Move right to left
for (int col = right; col >= left; col--) {
result.push_back(matrix[bottom][col]);
}
bottom--;
}
// Edge Case Check
if (left <= right) {
// Move bottom to top
for (int row = bottom; row >= top; row--) {
result.push_back(matrix[row][left]);
}
left++;
}
}
return result;
}
};
Time and Space Complexity
Time: O(m * n)
- Every element is visited exactly once.
Space: O(1) extra
- The output array is not counted.
Final Takeaways
- Break the problem into smaller steps.
- Edge condition checks (
top <= bottom,left <= right) are critical to avoid duplicates. - This approach works for non-square matrices too.